网站聊天系统怎么做如何查询关键词的搜索量
目录
栈
栈的概念及结构:
栈的实现:
代码实现:
Stack.h
stack.c
队列:
概念及结构:
队列的实现:
代码实现:
Queue.h
Queue.c
拓展:
循环队列(LeetCode题目链接):
-
栈
栈的概念及结构:
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。
进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
栈中的数据元素遵守“先进后出/后进先出”的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
“先进后出/后进先出”示意图: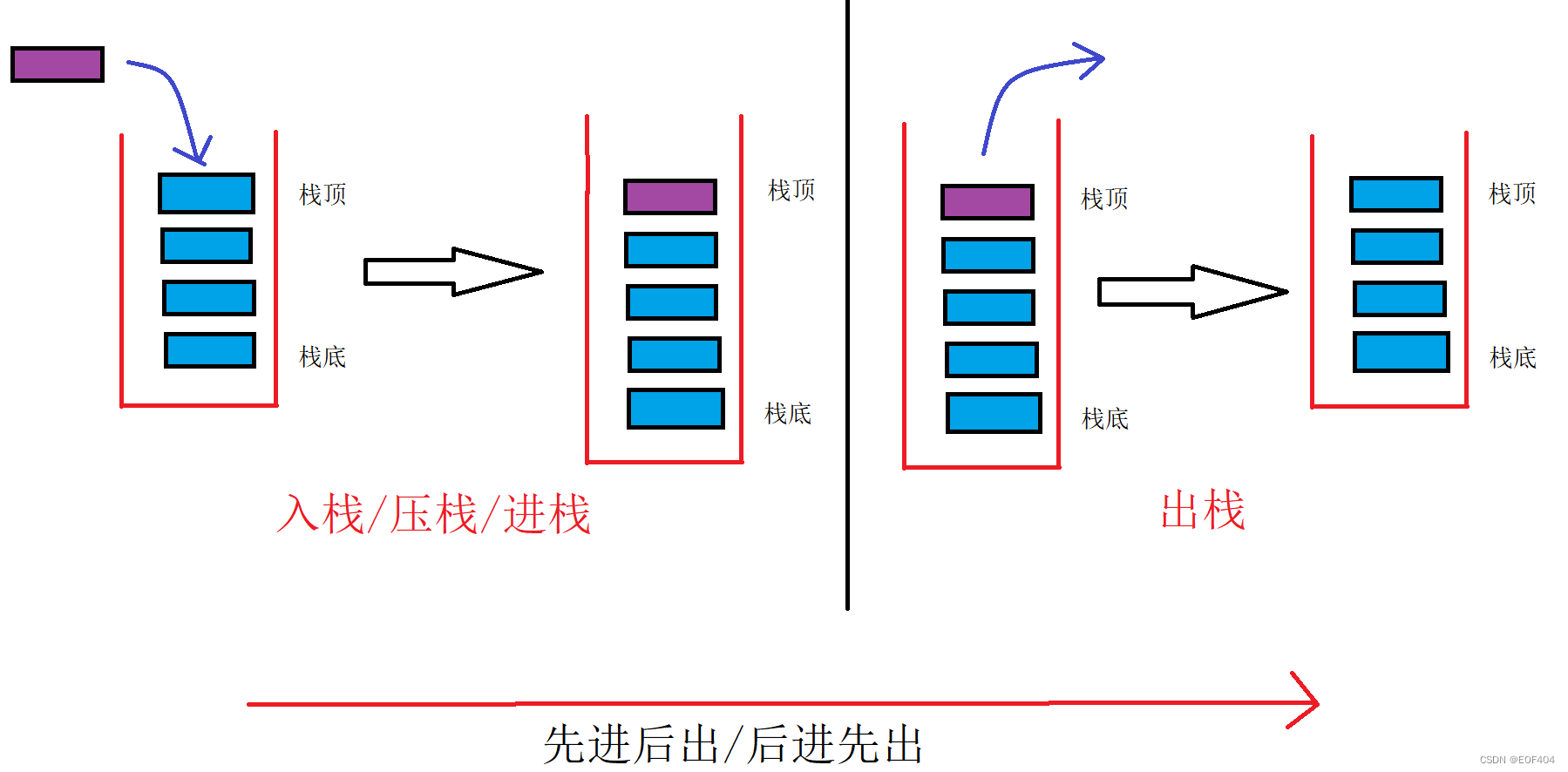
栈的实现:
一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
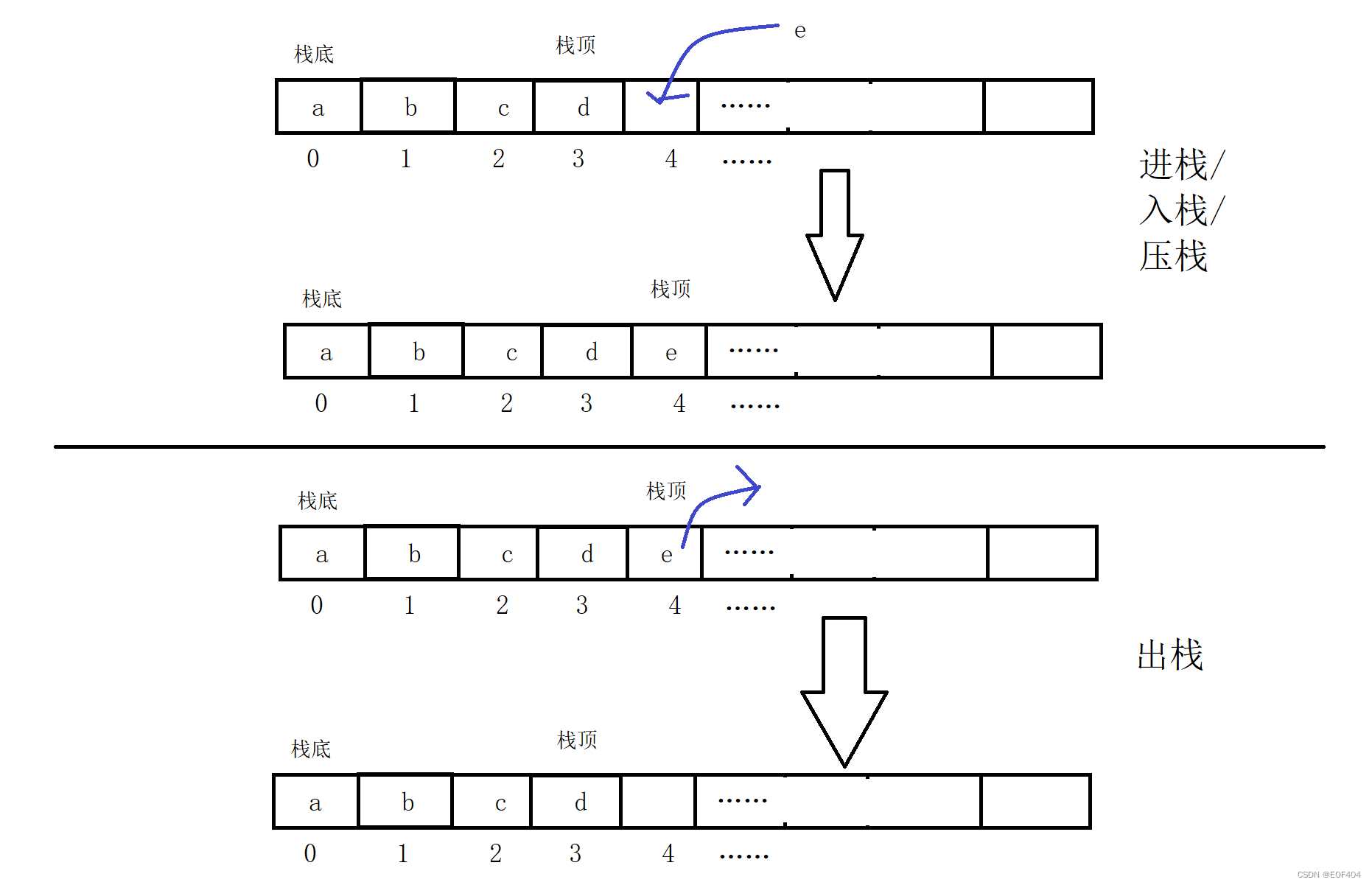
代码实现:
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;//栈顶int capacity;//容量
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
//入栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//出栈
void STPop(ST* ps);
//取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//数据个数
int STSize(ST* ps);
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);stack.c
#include"Stack.h"
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = 0;ps->top = 0;
}
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = 0;ps->top = 0;
}
//入栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->capacity == ps->top){int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* p = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);ps->a = p;ps->capacity = newcapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}//出栈
void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->a);assert(!STEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}
//取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->a);assert(!STEmpty(ps));return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//数据个数
int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->a);return ps->top;
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}测试代码:
#include"Stack.h"
int main()
{ST p1;STInit(&p1);int i = 0;//入栈for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++){STPush(&p1, i);}printf("栈中数据数量:%d\n", STSize(&p1));//出栈for (i = 0; i < 5; i++){STDataType a = STTop(&p1);printf("%d ", a);STPop(&p1);}printf("\n");printf("栈顶元素:%d\n", STTop(&p1));printf("栈中数据数量:%d\n", STSize(&p1));STDestroy(&p1);return 0;
}运行结果:

队列:
概念及结构:
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有“先 进先出/后进后出”的特点。
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾。
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
“先进先出/后进后出”示意图:
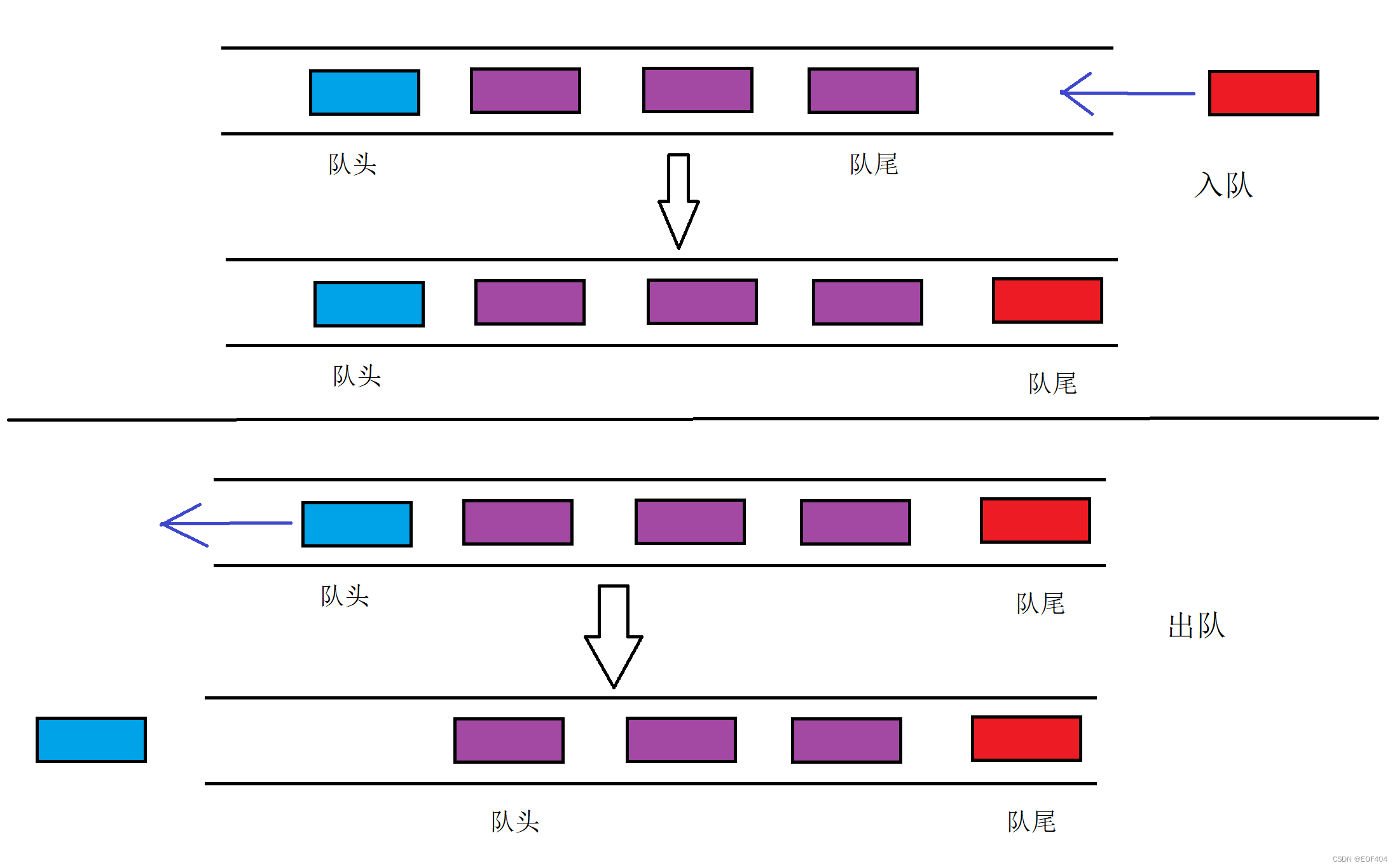
队列的实现:
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构在出队时的效率会比较低。
代码实现:
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Que;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Que* pq);
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq);
//入队
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x);
//出队
void QueuePop(Que* pq);
//取队头
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq);
//取队尾
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq);
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq);
//有效数据
int QueueSize(Que* pq);Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"//初始化
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* p = cur->next;free(cur);cur = p;}pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
//入队
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->head == NULL){pq->head = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}
//出队
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//要有数据if (pq->head->next == NULL)//只有一个节点{free(pq->head);pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* cur = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = cur;}pq->size--;
}
//取队头
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}
//取队尾
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}
//判空 :空返回1,非空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}
//有效数据
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}代码测试:
#include"Queue.h"
int main()
{Que p2;QueueInit(&p2);int i = 0;//入队for (i = 11; i <= 20; i++){QueuePush(&p2, i);}printf("队列中数据数量:%d\n", QueueSize(&p2));//出队for (i = 0; i < 7; i++){QDataType a = QueueFront(&p2);printf("%d ", a);QueuePop(&p2);}printf("\n");printf("队头元素:%d 队尾元素:%d\n", QueueFront(&p2), QueueBack(&p2));printf("队列中数据数量:%d\n", QueueSize(&p2));QueueDestroy(&p2);return 0;
}运行实例:

拓展:
循环队列(LeetCode题目链接):
循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于普通队列“先进先出”原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
循环队列可以使用数组实现,也可以使用循环链表实现。
以循环链表实现为例:
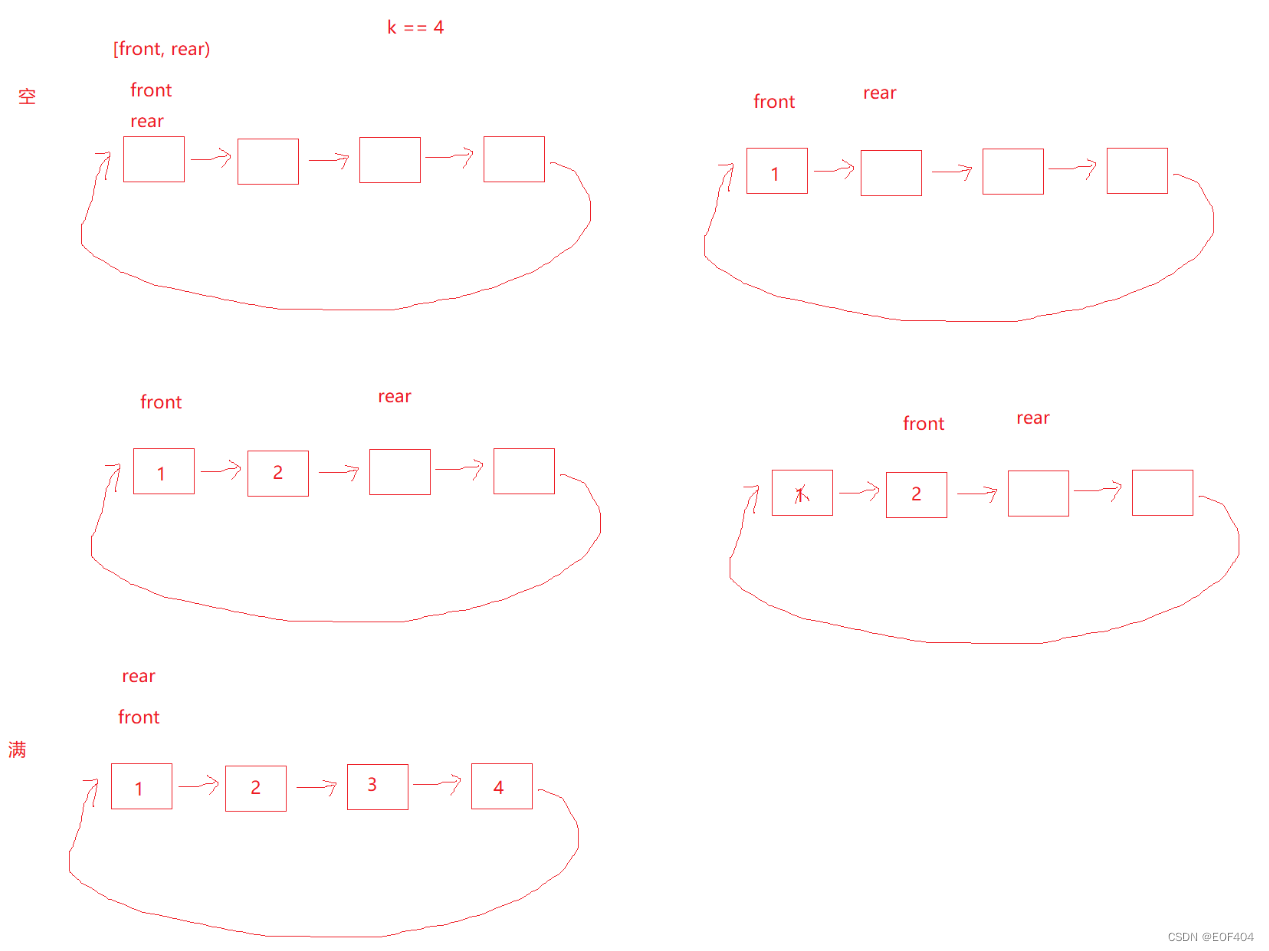
若仅仅是需要几个空间就创建几个空间,则空和满两种情况将无法区分,因此我们可以比实际需要多创建一个空间,这一个多创建出来空间不存储数据,则有如下情况:
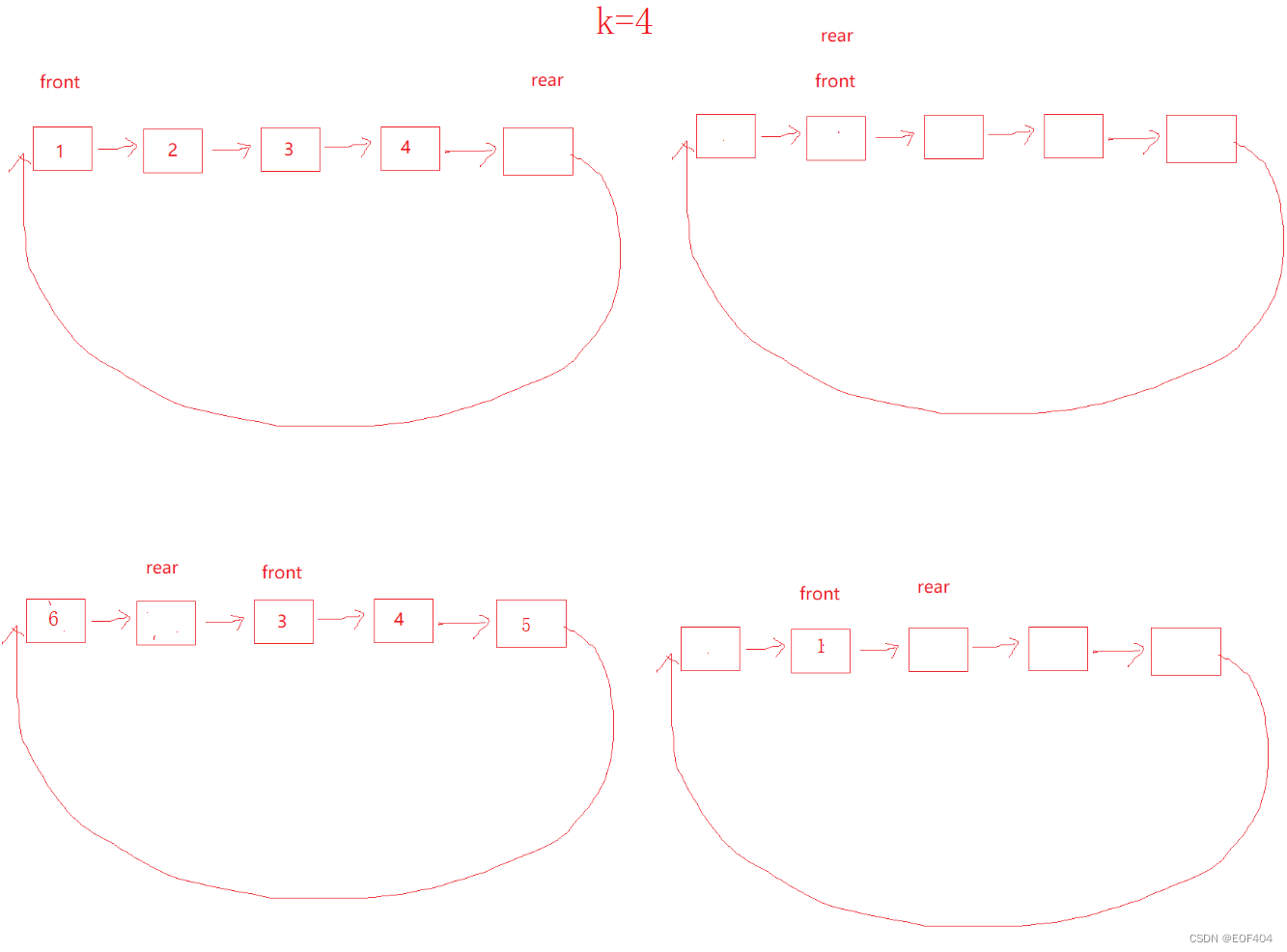
则满和空两种情况就可以区分出来了:front=rear-->空
rear的下一个=front-->满
同时为了方便取队尾数据,可以定义一个全局变量指向队尾位置(即rear指向位置的前一个)。
具体代码实现:
typedef struct List
{int val;struct List*next;
}list;
typedef struct
{list*front;list*rear;
} MyCircularQueue;
list*tail;//定义一个全局变量记录rear的前一个
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));if (obj == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}obj->front = NULL;obj->rear = NULL;int n = k + 1;while (n--){list* new = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));if (new == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}new->val = 0;new->next = obj->front;if (obj->front == NULL){obj->front = new;obj->rear = new;}else{obj->rear->next = new;tail=new;obj->rear = obj->rear->next;}} obj->rear=obj->front;return obj;
}
//判空:空返回真,非空返回假
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{return obj->front==obj->rear;
}
//是否已满:已满返回真,不满返回假
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{return obj->rear->next==obj->front;
}
//插入数据:插入成功返回真,失败返回假
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{assert(obj);if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))//已满{return false;}else{obj->rear->val=value;obj->rear=obj->rear->next;tail=tail->next;return true;}
}
//从队列中删除元素
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return false;}else{obj->front=obj->front->next;return true;}
}
//获取对首元素
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}return obj->front->val;
}
//获取队尾元素
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}/*list*cur=obj->front;while(cur->next!=obj->rear){cur=cur->next;}return cur->val;*/return tail->val;
}
//释放空间
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{while(obj->front!=obj->rear){list*Next=obj->front->next;free(obj->front);obj->front=Next;}free(obj->rear);free(obj);
}利用数组也可以实现,与链表类似在创建空间是同样需要多创建一个,但是因为队头、队尾没有链接关系,所以利用数组实现时与利用循环链表实现会有所不同:
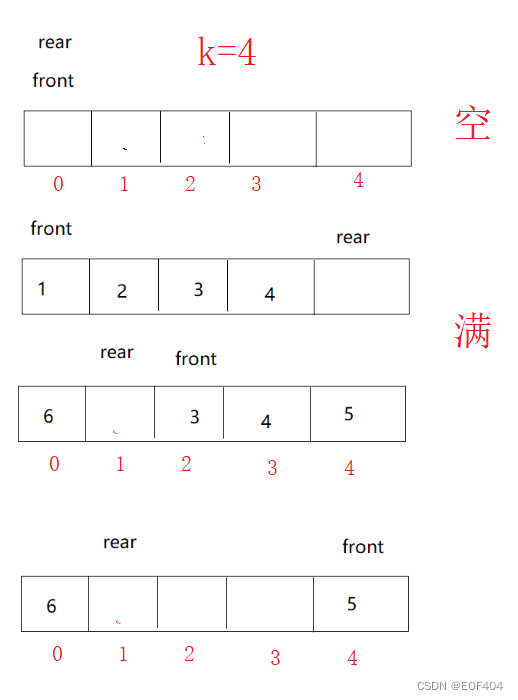
与循环链表类似,用数组实现循环队列时,当rear=front时,队列为空;在判断队列是否满时,虽然也是用rear的下一个等于front(即rear+1==front),但是不能单单使用 rear+1==front 判断,因为数组实现时,队首和队尾没有链接关系,当rear在数组最后一个位置时,循环队列已满,但rear+1会越界往后访问,且当front在数组最后一个位置时,删除数据后执行front+1也会出现越界访问的问题,出现错误,因此应想办法让rear和front都在数组范围内变化。
观察数组下标,可以让rear+1和front+1都模上k+1,问题就能很好解决。
具体代码实现:
typedef struct
{int k;int front;int rear;int* queue;
} MyCircularQueue;MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));if (obj == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}obj->k = k;obj->front = 0;obj->rear = 0;obj->queue = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (k + 1));if (obj->queue == NULL){perror("malloc failed");exit(-1);}return obj;
}
//判空:空返回真,非空返回假
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{return obj->rear == obj->front;
}
//是否已满:已满返回真,不满返回假
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{return (obj->rear + 1) % (obj->k + 1) == obj->front;
}
//插入数据:插入成功返回真,失败返回假
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{assert(obj);if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))//已满{return false;}else{obj->queue[obj->rear] = value;obj->rear = (obj->rear + 1) % (obj->k + 1);return true;}
}
//从队列中删除元素
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return false;}else{obj->front = (obj->front + 1) % (obj->k + 1);return true;}
}
//获取对首元素
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}return obj->queue[obj->front];
}
//获取队尾元素
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}return obj->queue[(obj->rear + obj->k) % (obj->k + 1)];
}
//释放空间
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{free(obj->queue);obj->queue = NULL;free(obj);
}