赤坎手机网站建设公司移动优化课主讲:夫唯老师
文章目录
- 一、poll的认识
- 二、编写poll方案服务器
- 三、poll方案多路转接的总结
一、poll的认识
多路转接技术是在不断更新进步的,一开始多路转接采用的是select方案,但是select方案存在的缺点比较多,所以在此基础上改进,产生了poll方案。poll是多路转接的另一种方案,它使用起来比select方案简单很多,也比较好用。
poll函数原型:
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
select方案的最大缺点就在于它的输入和输出都是用同一个参数,比如我们将设置好的需要等待的文件描述符集合输入进去使用的是readfds这个参数,它将文件描述符集合中读事件就绪的文件描述符输出出来也是使用readfds这个参数。这就导致我们每一次都需要重置参数,所以这给我们使用select增加了很大的成本。并且fd_set是位图结构,所以就导致select函数可以检测的文件描述符数量是有上限的。
针对select方案的上述缺点,poll进行了改进:poll的参数struct pollfd *fds其实是一个结构体数组,它里面的结构如下图所示:
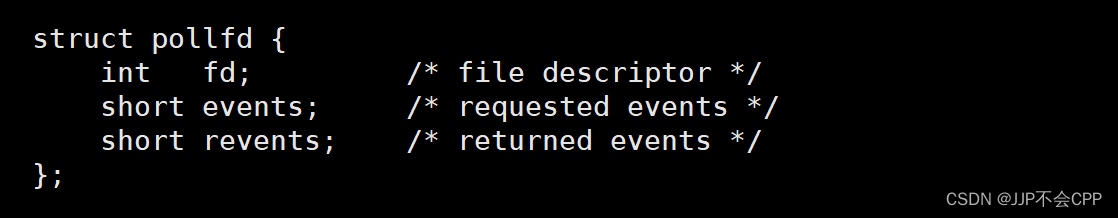
其中fd表示要等待的文件描述符是什么,events表示我们要传递进去的等待事件是什么,revents表示内核给我们传递出来的事件。这个结构和select就有很大的差别,它把原来select的readfds拆分成了两个参数,将输入和输出进行了分离。第二个参数nfds_t nfds其实就是一个整数,代表结构体数组的元素个数。第三个参数int timeout代表等待时间,当该参数设置为-1时代表永久阻塞,当该参数设置为0时代表非阻塞,当该参数设置大于0时代表在规定时间内阻塞,超时之后返回0。
pollfd结构体中的events和revents可以设置不同的事件,它们常用的取值有:
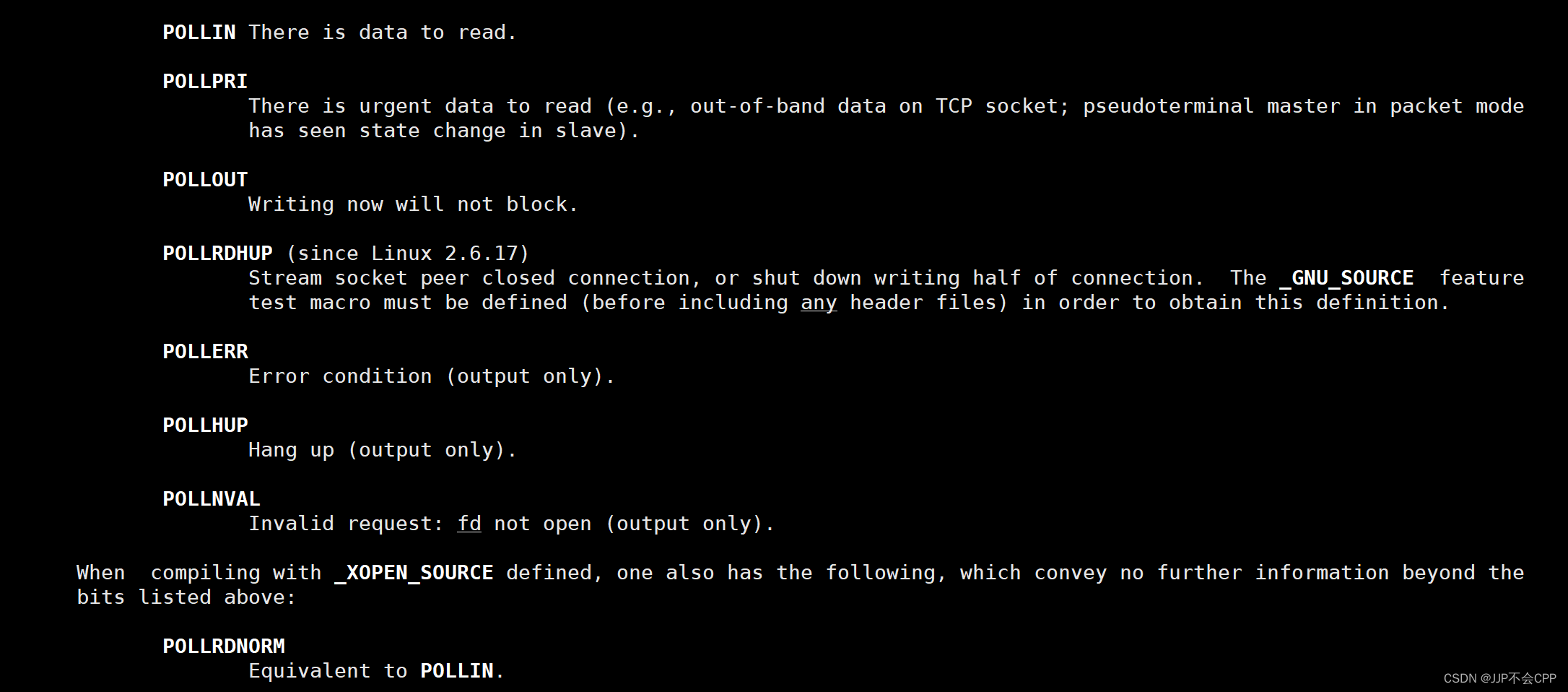
二、编写poll方案服务器
我们可以编写一个poll方案的多路转接服务器,来演示一下poll函数接口的使用:
Sock.hpp:
#pragma once#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <cerrno>
#include <cassert>class Sock
{
public:static const int gbacklog = 20;static int Socket(){int listenSock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);if (listenSock < 0){exit(1);}int opt = 1;setsockopt(listenSock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR | SO_REUSEPORT, &opt, sizeof(opt));return listenSock;}static void Bind(int socket, uint16_t port){struct sockaddr_in local; // 用户栈memset(&local, 0, sizeof local);local.sin_family = PF_INET;local.sin_port = htons(port);local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;// 2.2 本地socket信息,写入sock_对应的内核区域if (bind(socket, (const struct sockaddr *)&local, sizeof local) < 0){exit(2);}}static void Listen(int socket){if (listen(socket, gbacklog) < 0){exit(3);}}static int Accept(int socket, std::string *clientip, uint16_t *clientport){struct sockaddr_in peer;socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);int serviceSock = accept(socket, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, &len);if (serviceSock < 0){// 获取链接失败return -1;}if(clientport) *clientport = ntohs(peer.sin_port);if(clientip) *clientip = inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr);return serviceSock;}
};
PollServer.cc:
#include <iostream>
#include <poll.h>
#include "Sock.hpp"#define NUM 1024
struct pollfd fdsArray[NUM]; // 保存历史上所有的合法fd#define DFL -1using namespace std;static void showArray(struct pollfd arr[], int num)
{cout << "当前合法sock list# ";for (int i = 0; i < num; i++){if (arr[i].fd == DFL)continue;elsecout << arr[i].fd << " ";}cout << endl;
}static void usage(std::string process)
{cerr << "\nUsage: " << process << " port\n"<< endl;
}
// readfds: 现在包含就是已经就绪的sock
static void HandlerEvent(int listensock)
{for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){if (fdsArray[i].fd == DFL)continue;if (i == 0 && fdsArray[i].fd == listensock){// 我们是如何得知哪些fd,上面的事件就绪呢?if (fdsArray[i].revents & POLLIN){// 具有了一个新链接cout << "已经有一个新链接到来了,需要进行获取(读取/拷贝)了" << endl;string clientip;uint16_t clientport = 0;int sock = Sock::Accept(listensock, &clientip, &clientport); // 不会阻塞if (sock < 0)return;cout << "获取新连接成功: " << clientip << ":" << clientport << " | sock: " << sock << endl;// read/write -- 不能,因为你read不知道底层数据是否就绪!!select知道!// 想办法把新的fd托管给select?如何托管??int i = 0;for (; i < NUM; i++){if (fdsArray[i].fd == DFL)break;}if (i == NUM){cerr << "我的服务器已经到了最大的上限了,无法在承载更多同时保持的连接了" << endl;close(sock);}else{fdsArray[i].fd = sock; // 将sock添加到select中,进行进一步的监听就绪事件了!fdsArray[i].events = POLLIN;fdsArray[i].revents = 0;showArray(fdsArray, NUM);}}} // end if (i == 0 && fdsArray[i] == listensock)else{// 处理普通sock的IO事件!if(fdsArray[i].revents & POLLIN){// 一定是一个合法的普通的IO类sock就绪了// read/recv读取即可// TODO bugchar buffer[1024];ssize_t s = recv(fdsArray[i].fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0); // 不会阻塞if(s > 0){buffer[s] = 0;cout << "client[" << fdsArray[i].fd << "]# " << buffer << endl; }else if(s == 0){cout << "client[" << fdsArray[i].fd << "] quit, server close " << fdsArray[i].fd << endl;close(fdsArray[i].fd);fdsArray[i].fd = DFL; // 去除对该文件描述符的select事件监听fdsArray[i].events = 0;fdsArray[i].revents = 0;showArray(fdsArray, NUM);}else{cout << "client[" << fdsArray[i].fd << "] quit, server error " << fdsArray[i].fd << endl;close(fdsArray[i].fd);fdsArray[i].fd = DFL; // 去除对该文件描述符的select事件监听fdsArray[i].events = 0;fdsArray[i].revents = 0;showArray(fdsArray, NUM);}}}}
}// ./SelectServer 8080
// 只关心读事件
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if (argc != 2){usage(argv[0]);exit(1);}// 是一种类型,位图类型,能定义变量,那么就一定有大小,就一定有上限// fd_set fds; // fd_set是用位图表示多个fd的// cout << sizeof(fds) * 8 << endl;int listensock = Sock::Socket();Sock::Bind(listensock, atoi(argv[1]));Sock::Listen(listensock);for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){fdsArray[i].fd = DFL;fdsArray[i].events = 0;fdsArray[i].revents = 0;}fdsArray[0].fd = listensock;fdsArray[0].events = POLLIN;int timeout = -1;while (true){int n = poll(fdsArray, NUM, timeout);switch (n){case 0:cout << "time out ... : " << (unsigned long)time(nullptr) << endl;break;case -1:cerr << errno << " : " << strerror(errno) << endl;break;default:HandlerEvent(listensock);// 等待成功// 1. 刚启动的时候,只有一个fd,listensock// 2. server 运行的时候,sock才会慢慢变多// 3. select 使用位图,采用输出输出型参数的方式,来进行 内核<->用户 信息的传递, 每一次调用select,都需要对历史数据和sock进行重新设置!!!// 4. listensock,永远都要被设置进readfds中!// 5. select 就绪的时候,可能是listen 就绪,也可能是普通的IO sock就绪啦!!break;}}return 0;
}
三、poll方案多路转接的总结
poll方案的优点:
poll方案的多路转接不同于select方案的多路转接使用三个位图来表示三个fdset的方式,poll使用一个pollfd的指针来实现,这个指针其实是一个结构体数组。
pollfd结构体里包含了要监视的event和发送的event,不再使用select的那种输入输出采用同一个参数的方式,因此poll函数接口使用起来比select要简单方便。
除此之外,poll方案并没有最大的数量限制,pollfd这个结构体数组的元素个数是由我们用户自己决定的,它不像select那样采用位图结构,规定了最大数量限制就是1024。但是poll方案数量过大之后性能也是会下降的。
poll方案的缺点:
poll函数和select函数一样,poll函数返回后都需要轮询检测pollfd来获取就绪的文件描述符,当pollfd中监听的文件描述符数目增多时,性能也会下降。
每次调用poll函数都需要把大量的pollfd结构从用户态拷贝到内核态,这也会因为pollfd结构数组中元素个数过多时导致性能下降。
同时连接的大量客户端在一时刻可能只有很少的处于就绪状态,因此随着监视的文件描述符数量的增长,其效率也会线性下降。
